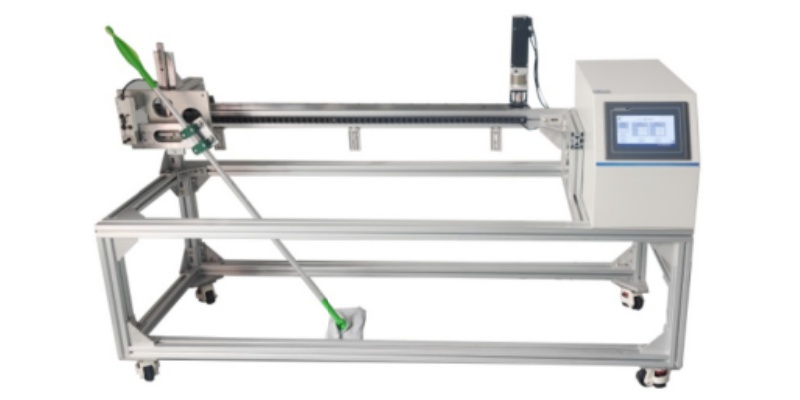
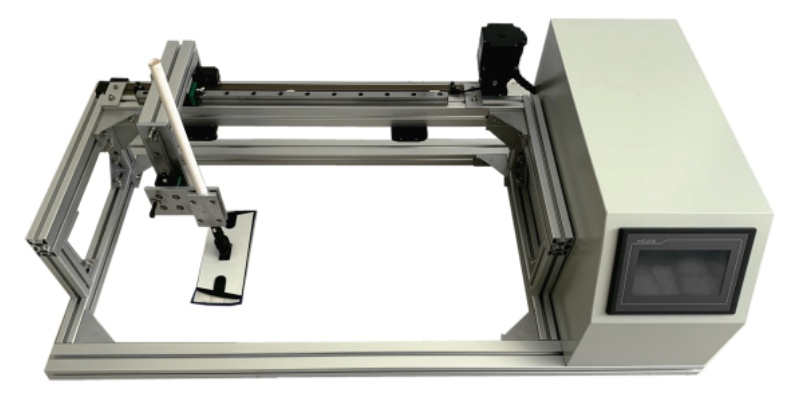
Ελεγκτής θερμικής συρρίκνωσης νήματος
Δοκιμή υλικού σφουγγαρίστρας
-Δοκιμή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης
Η δοκιμή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης νήματος είναι ζωτικής σημασίας για τη διασφάλιση της καλής απόδοσης των προϊόντων νήματος κατά τη διάρκεια της διαδικασίας κατασκευής και τελικής χρήσης τους. Εάν το υλικό (νήμα ή ύφασμα) πρόκειται να χρησιμοποιηθεί για σφουγγάρισμα, τότε το Yarn Thermal Shrinkage Testing by ASTM D4974 γίνεται ακόμη πιο σημαντικό.
Η σημασία της δοκιμής θερμικής συρρίκνωσης για υλικά σφουγγαρίστρας
Στη βιομηχανία σφουγγαρίστρας, τα νήματα που χρησιμοποιούνται στις κεφαλές σφουγγαρίστρας συχνά εκτίθενται σε ζεστό νερό και άλλα σκληρά καθαριστικά. Αυτή η έκθεση μπορεί να προκαλέσει τη συρρίκνωση του νήματος, επηρεάζοντας την αποτελεσματικότητα και τη μακροζωία της σφουγγαρίστρας.
Γιατί έχει σημασία η δοκιμή συρρίκνωσης
Τα νήματα που κατασκευάζονται από υλικά όπως ο πολυεστέρας και το νάιλον μπορεί να συρρικνωθούν όταν εκτεθούν στη θερμότητα, γεγονός που θα μπορούσε να θέσει σε κίνδυνο τη δομή του υλικού σφουγγαρίστρας. Η δοκιμή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης διασφαλίζει ότι τα νήματα και τα κορδόνια διατηρούν τη σταθερότητα των διαστάσεων τους, αποτρέποντας ζητήματα όπως:
- Μειωμένη περιοχή κάλυψης σφουγγαρίστρας
- Μειωμένη αποτελεσματικότητα καθαρισμού
- Μειωμένη διάρκεια ζωής της κεφαλής σφουγγαρίστρας
Τεχνικά χαρακτηριστικά του δοκιμαστή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης νήματος
| Προϋποθέσεις χρήσης | -10~40℃, RH: 45%~85%, χωρίς κραδασμούς |
| Εύρος θερμοκρασίας και ακρίβεια | Περιβάλλον~250°C; ±0,1°C |
| Ανάλυση συρρίκνωσης | 0,01% (100% είναι 250mm) |
| Ανάλυση δύναμης συρρίκνωσης | 0,01Ν |
| Εύρος δυνάμεων συρρίκνωσης | 0~50N (Διαθέσιμη προσαρμογή) |
| Ώρα δοκιμής | 0,1~60 λεπτά |
| Εξουσία | AC220V, 50Hz |
| Μέγιστη ισχύς θέρμανσης | 1000W |
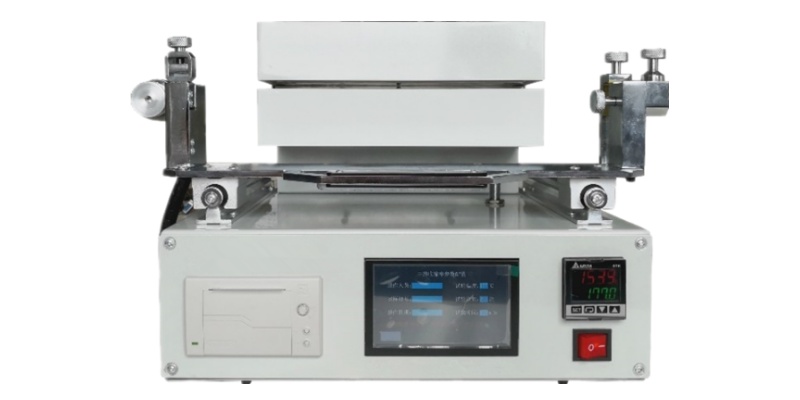

Γιατί χρειάζεται δοκιμή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης
Πρόληψη παραμόρφωσης
Οι σφουγγαρίστρες απαιτούν συχνά το υλικό να είναι ιδιαίτερα απορροφητικό και να διατηρεί το σχήμα του για αποτελεσματικότητα τριψίματος. Η θερμική συρρίκνωση μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε ανομοιόμορφη συρρίκνωση του υφάσματος, προκαλώντας συρρίκνωση ή παραμόρφωση. Η δοκιμή διασφαλίζει ότι το νήμα συμπεριφέρεται προβλέψιμα όταν εκτίθεται στη θερμότητα, αποφεύγοντας αυτά τα ζητήματα.
Βελτιωμένη μακροζωία
Η τακτική έκθεση σε υψηλές θερμοκρασίες, διαλύματα καθαρισμού και μηχανική φθορά μπορεί να προκαλέσει το ύφασμα να χάσει τη μορφή του. Η συρρίκνωση μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε χαλάρωση των ινών, με αποτέλεσμα την ταχύτερη φθορά. Χρησιμοποιώντας νήμα που έχει δοκιμαστεί για θερμική συρρίκνωση, οι κατασκευαστές μπορούν να παράγουν πιο ανθεκτικές σφουγγαρίστρες που διαρκούν περισσότερο κάτω από σκληρές συνθήκες καθαρισμού.
Ικανοποίηση πελατών
Για τους πελάτες, μια σφουγγαρίστρα που συρρικνώνεται ή χάνει το σχήμα της μετά το πλύσιμο δεν θα έχει την αναμενόμενη απόδοση, οδηγώντας σε δυσαρέσκεια και αυξημένο κόστος αντικατάστασης. Η δοκιμή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης βοηθά τους κατασκευαστές να διασφαλίσουν ότι η σφουγγαρίστρα διατηρεί το προβλεπόμενο μέγεθος, το σχήμα και τη λειτουργία της με την πάροδο του χρόνου, μειώνοντας τα παράπονα των πελατών και βελτιώνοντας τη φήμη του προϊόντος.
Ανθεκτικότητα κάτω από τη θερμότητα
Οι σφουγγαρίστρες χρησιμοποιούνται συχνά σε περιβάλλοντα με υψηλή θερμότητα (όπως κουζίνες, βιομηχανικές περιοχές ή νοσοκομεία) και το νήμα ή το ύφασμα πρέπει να αντέχουν τόσο τη μηχανική καταπόνηση του σφουγγάρισμα όσο και τη θερμότητα από το πλύσιμο ή το στέγνωμα. Η δοκιμή από το ASTM D4974 βοηθά τους κατασκευαστές να επιβεβαιώσουν ότι το νήμα διατηρεί την αντοχή και τη δομή του όταν εκτίθεται σε ζεστό νερό ή σε υψηλές θερμοκρασίες στεγνώματος, διασφαλίζοντας ότι η σφουγγαρίστρα λειτουργεί με συνέπεια.
Σταθερότητα διαστάσεων μετά το πλύσιμο
Οι σφουγγαρίστρες συνήθως πλένονται συχνά και εκτίθενται σε υψηλές θερμοκρασίες (π.χ. ζεστό νερό για απολύμανση). Η δοκιμή για θερμική συρρίκνωση διασφαλίζει ότι το υλικό δεν θα συρρικνωθεί σημαντικά μετά το πλύσιμο, διατηρώντας το μέγεθος και την αποτελεσματικότητα της σφουγγαρίστρας για τον καθαρισμό. Η υπερβολική συρρίκνωση θα μπορούσε να καταστήσει τη σφουγγαρίστρα αναποτελεσματική ή να την κάνει να παραμορφωθεί, γεγονός που επηρεάζει την απόδοση και τη διάρκεια ζωής της.
Δοκιμή υλικού σφουγγαρίστρας και θερμική συρρίκνωση
Για υλικά σφουγγαρίστρας, ιδιαίτερα εκείνα που ενσωματώνουν συνθετικά νήματα όπως πολυεστέρας και νάιλον, η δοκιμή του υλικού σφουγγαρίστρας για συρρίκνωση είναι κρίσιμη. Οι κεφαλές σφουγγαρίστρας υποβάλλονται σε συχνό πλύσιμο, συχνά σε υψηλές θερμοκρασίες, γεγονός που μπορεί να προκαλέσει σημαντική συρρίκνωση στις ίνες. Διεξάγοντας δοκιμές θερμικής συρρίκνωσης χρησιμοποιώντας έναν ελεγκτή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης, οι κατασκευαστές μπορούν:
- Προσδιορίστε τη θερμική αντίσταση των νημάτων που χρησιμοποιούνται στις κεφαλές σφουγγαρίστρας
- Βεβαιωθείτε ότι τα νήματα διατηρούν το μέγεθος και το σχήμα τους μετά από επαναλαμβανόμενους κύκλους πλύσης
- Βελτιστοποιήστε τη σύνθεση και την ποιότητα των υλικών σφουγγαρίστρας για να παρατείνετε τον κύκλο ζωής τους
- Αυτή η διαδικασία διασφαλίζει ότι το τελικό προϊόν - η κεφαλή σφουγγαρίστρας - θα λειτουργεί αποτελεσματικά με την πάροδο του χρόνου χωρίς να χάσει τη λειτουργικότητά του λόγω συρρίκνωσης.
Ελεγκτής θερμικής συρρίκνωσης - Πρότυπο ASTM D4974

Βήμα προς βήμα διαδικασία δοκιμής θερμικής συρρίκνωσης (ASTM D4974)
- Προετοιμασία δείγματος: Το νήμα ή το κορδόνι χαλαρώνει στη φυσική του κατάσταση πριν ξεκινήσει η δοκιμή.
- Ρύθμιση δοκιμής: Το δείγμα τοποθετείται υπό ελεγχόμενη τάση εντός του ελεγκτή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης.
- Έκθεση στη θερμότητα: Το νήμα ή το κορδόνι υποβάλλεται σε ξηρή θερμότητα για καθορισμένη διάρκεια σε ρυθμιζόμενη θερμοκρασία.
- Μέτρηση: Ο ελεγκτής θερμικής συρρίκνωσης υπολογίζει τον ρυθμό συρρίκνωσης, που συνήθως εκφράζεται ως ποσοστό του αρχικού μήκους του υλικού.
- Ανάλυση Αποτελεσμάτων: Τα τελικά αποτελέσματα παρέχουν πολύτιμα δεδομένα για τη δύναμη και το ρυθμό θερμικής συρρίκνωσης του υλικού, βοηθώντας τους κατασκευαστές να αξιολογήσουν την απόδοση του νήματος ή του κορδονιού υπό έκθεση σε θερμότητα.
Συχνές ερωτήσεις σχετικά με τη δοκιμή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης
1. Ποιοι τύποι υλικών μπορούν να ελεγχθούν χρησιμοποιώντας έναν ελεγκτή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης;
Ένας ελεγκτής θερμικής συρρίκνωσης μπορεί να δοκιμάσει διάφορα νήματα και κορδόνια κατασκευασμένα από υλικά όπως νάιλον, πολυεστέρας, αραμίδιο και άλλα.
2. Ποια είναι η διαφορά μεταξύ ASTM D4974 και ASTM D5591 στη δοκιμή θερμικής συρρίκνωσης;
Το ASTM D4974 εστιάζει στη μέτρηση του ρυθμού συρρίκνωσης υπό ελεγχόμενη τάση, ενώ το ASTM D5591 μετρά τη δύναμη συρρίκνωσης που προκαλείται από την έκθεση στη θερμότητα.
3. Μπορεί ένας ελεγκτής θερμικής συρρίκνωσης να βοηθήσει στη μείωση των ελαττωμάτων στη δοκιμή υλικού σφουγγαρίστρας;
Ναι, με τον έγκαιρο εντοπισμό πιθανών προβλημάτων συρρίκνωσης, οι δοκιμές θερμικής συρρίκνωσης βοηθούν τους κατασκευαστές να παράγουν υλικά σφουγγαρίστρας υψηλής ποιότητας που έχουν σταθερή απόδοση με την πάροδο του χρόνου.
Σχετική λύση ποιοτικού ελέγχου σφουγγαρίστρας
Ψάχνετε για αξιόπιστο Tester Θερμικής Συρρίκνωσης Νήματος;
Μην χάσετε την ευκαιρία να βελτιστοποιήσετε τις διαδικασίες ποιοτικού ελέγχου σας με εξοπλισμό τελευταίας τεχνολογίας.